CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Syllabus
CLASS-XII Mathematics COURSE STRUCTURE-
One Paper Max Marks: 80
|
No. |
Units |
No. of Periods |
Marks |
|
I. |
Relations and Functions |
30 |
08 |
|
II. |
Algebra |
50 |
10 |
|
III. |
Calculus |
80 |
35 |
|
IV. |
Vectors and Three – Dimensional Geometry |
30 |
14 |
|
V. |
Linear Programming |
20 |
05 |
|
VI. |
Probability |
30 |
08 |
|
|
Total |
240 |
80 |
|
|
Internal Assessment |
|
20 |
Detailed Syllabus Mathematics Class 11-
Unit-I: Relations and Functions
- Relations and Functions 15 Periods
Types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive and equivalence relations. One to one and onto functions.
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions 15 Periods Definition, range, domain, principal value branch. Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions. Unit-II: Algebra
1. Matrices 25 Periods
Concept, notation, order, equality, types of matrices, zero and identity matrix, transpose of a matrix, symmetric and skew symmetric matrices. Operations on matrices: Addition and multiplication and multiplication with a scalar. Simple properties of addition, multiplication and scalar multiplication. Non- commutativity of multiplication of matrices and existence of non-zero matrices whose product is the zero matrix (restrict to square matrices of order 2). Invertible matrices and proof of the uniqueness of inverse, if it exists; (Here all matrices will have real entries).
2. Determinants 25 Periods
Determinant of a square matrix (up to 3 x 3 matrices), minors, co-factors and applications of determinants in finding the area of a triangle. Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix. Consistency, inconsistency and number of solutions of system of linear equations by examples, solving system of linear equations in two or three variables (having unique solution) using inverse of a matrix.
Unit-III: Calculus
- Continuity and Differentiability 20 Periods
Continuity and differentiability, chain rule, derivative of inverse trigonometric functions,
𝑙𝑖𝑘𝑒 sin−1 𝑥 , cos−1 𝑥 and tan−1 𝑥, derivative of implicit functions. Concept of exponential and logarithmic functions.
Derivatives of logarithmic and exponential functions. Logarithmic differentiation, derivative of functions expressed in parametric forms. Second order derivatives.
- Applications of Derivatives 10 Periods Applications of derivatives: rate of change of quantities, increasing/decreasing functions, maxima and minima (first derivative test motivated geometrically and second derivative test given as a provable tool). Simple problems (that illustrate basic principles and understanding of the subject as well as real- life situations).
3. Integrals 20 Periods
Integration as inverse process of differentiation. Integration of a variety of functions by substitution, by partial fractions and by parts, Evaluation of simple integrals of the following types and problems based on them.
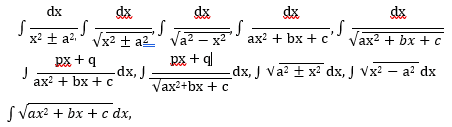
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (without proof). Basic properties of definite integrals and evaluation of definite integrals.
4. Applications of the Integrals 15 Periods
Applications in finding the area under simple curves, especially lines, circles/ parabolas/ellipses (in standard form only)
5. Differential Equations 15 Periods
Definition, order and degree, general and particular solutions of a differential equation. Solution of differential equations by method of separation of variables, solutions of homogeneous differential equations of first order and first degree. Solutions of linear differential equation of the type:
dy dx d𝑥 d𝑦
+ py = q, where p and q are functions of x or constants.
+ px = q, where p and q are functions of y or constants.
Unit-IV: Vectors and Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Vectors 15 Periods
Vectors and scalars, magnitude and direction of a vector. Direction cosines and direction ratios of a vector. Types of vectors (equal, unit, zero, parallel and collinear vectors), position vector of a point, negative of a vector, components of a vector, addition of vectors, multiplication of a vector by a scalar, position vector of a point dividing a line segment in a given ratio. Definition, Geometrical Interpretation, properties and application of scalar (dot) product of vectors, vector (cross) product of vectors.
- Three – dimensional Geometry 15 Periods Direction cosines and direction ratios of a line joining two Cartesian equation and vector equation of a line, skew lines, shortest distance between two lines. Angle between two lines.
Unit-V: Linear Programming
- Linear Programming 20 Periods
Introduction, related terminology such as constraints, objective function, optimization, graphical method of solution for problems in two variables, feasible and infeasible regions (bounded or unbounded), feasible and infeasible solutions, optimal feasible solutions (up to three non-trivial constraints).
Unit-VI: Probability
- Probability 30 Periods
Conditional probability, multiplication theorem on probability, independent events, total probability, Bayes’ theorem, Random variable and its probability distribution, mean of random variable.
